A human brain is called as a supercomputer! There is no doubt why it is named so! Midbrain is comparable to the internet that transfers audio and visual inputs from cortex to the brain. Midbrain is the middle part of the brain and acts as a bridge between the hindbrain and the forebrain. It integrates sensory information and enables the body to use information and adjust itself accordingly.
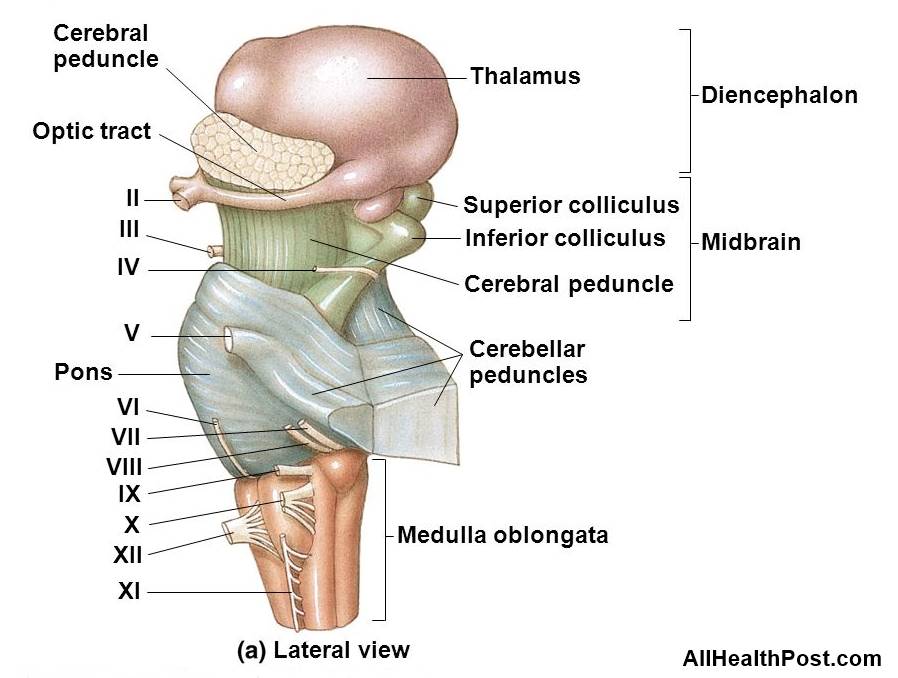
It is the part that is commonly known as the human brain or the supercomputer. The hindbrain is the back side of the main brain that comprises of the Pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum. It is the part that controls the primary instincts of a human body. It also controls the automated action, such as blood flow, heart rate, fight, body pressure, etc.
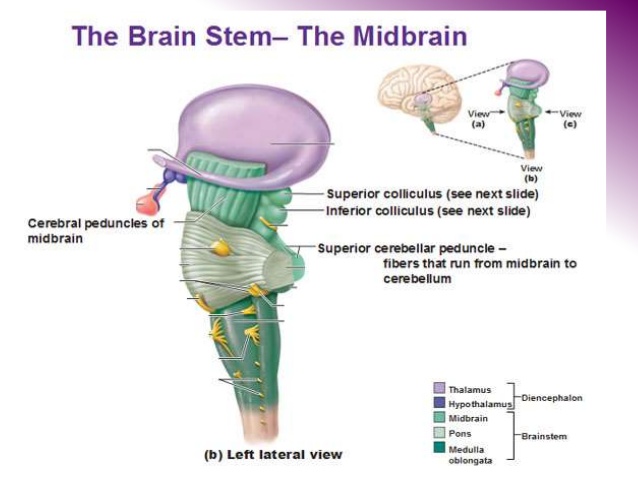
The midbrain is subsequently the highway between the two parts of the brain. Midbrain divides the brain into three main structures; Corpora quadrigemina, Cerebral Peduncle and the cerebral aqueduct. In this article, we will discuss the structure and functions of Cerebral Peduncle.
Topics Covered
What is Cerebral Peduncle?
The Cerebral Peduncle is also known as Cerebral Crus. The term cerebral stands for brain and Peduncle is a stem-like a connector. It is that part of the midbrain, which arises from the front part of the pon. It is a mass of neuron fibers positioned at the base of the brain. The large ascending and descending nerve tracts stretch from the cerebrum to the pons. They are the chief connectors between the spinal cord and midbrain.
The bundle of fibers contains axons of pyramidal cells to transport nerve impulses from the higher part of the brain to the lower parts. The axon fibers connect the cortex and other areas of the nervous systems.
The peduncles help in accepting the commands and movement of the body. They adjust the movements and manages the speed in which the specific part of the body moves. Cerebral Penducle detects any injury in the body and further guides that part to refine the movements.

To put it simply, Cerebral Penducle is located on both sides of the midbrain and acts as a connector between the midbrain and thalamic nuclei. It assists in motor movement, learning new skills and guiding the body to balance the structure. Any damage caused to the Cerebral Penducle leads to unrefined motor skills, imbalance posture and lack of understanding commands.
Structure of the Cerebral Peduncle?
The cerebral peduncle is a cylindrical bundle of nerves that resembles a footstalk. The fiber bands that run along the cerebral peduncle are divided into three; corticospinal, corticobulbar and corticopontine. The descending motor fibers arise from the internal capsule (cerebral hemisphere) and end in the midbrain. The outer and inner third of cerebral peduncle is made of corticopontine fibers traits. They act as cortical input for the pontine nuclei. The middle of the cerebral peduncle is formed of corticobulbar. The internal capsule consists of corticospinal in the cerebral peduncle.
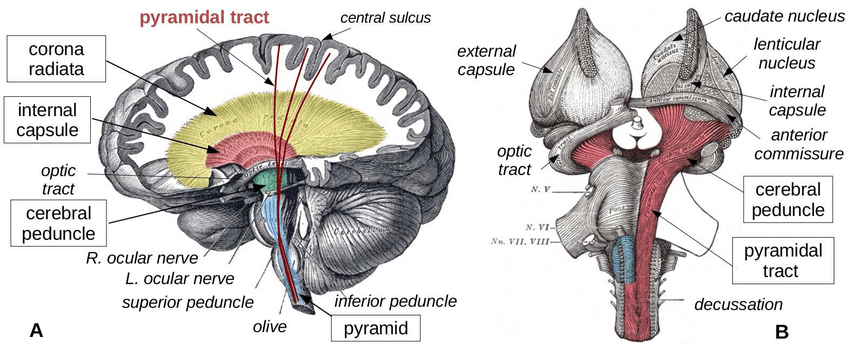
The Structure of the Cerebral is Divided Into Main Parts: Cerebral Crus and Tegmento.
Cerebral Crus:
The Cerebral Crus is the front part of the cerebral peduncle that controls the movement of the body. It transmits the brain information regarding each body parts and controls the motor movement accordingly. The information that arises from the cerebral crus is basically a conscious decision carried to the cortex defining the current status of the body.
Tegmento:
Tegmento is the cover of the cerebral nerves. It is a structure of embryonic development and establishes communication between the cortex and the trunk of the brain. It basically acts as a carrier that sends and receives information from other parts of the brain.
Functions of the Cerebral Peduncle
The main function of cerebral peduncle is transferring motor signals from the cortex to the spinal cord. Simply put, the functions are divided into two main functions- development of reflex movements and conduction of movements.
The cerebral peduncle is the basic part that acts as the bridge between other parts of the midbrain and the main brain. Cerebral Peduncle controls the motor skills of the body and transmits the data to the brain. The brain then gets information on how to control the body movements accordingly. In the same manner, the cerebral transfers the information from the brain to the specific parts of the body.
Additionally, there is something called the red nucleus that communicates cerebellum with the cerebral peduncle. It fine-tunes the communication and the motor movements commonly known as proprioception.
Proprioception is the sense of self-environment which allows you to feel your own body parts with blindfolds. In case of damaged cerebral peduncles, the sense of proprioception fails and leads to clumsiness and graceless feelings.
Each human brain is united by the interpeduncular fossa that comprises of cranial nerves. There is two pair of cranial nerves (3 and 4) that originates from the cerebral. The cranial 3 lies between the two cerebral peduncles. Otherwise known as oculomotor nerve, cranial nerves 4 wraps around the lowest part of the cerebral peduncle. The intervention of nerves allows you to sync your eyes with the movement of head and neck. It means when you want to look at a certain side; your eye sockets help you to see the objects without swinging your head.
Conclusion
The cerebral peduncle is a paired structure that intervenes between the brain and the body. They help to transport nerve impulses from the higher part of the brain (the cortex) to the lower part of the brain stem. It also transmits the reflex impulses to other nervous systems. It helps to refine your body movements and transmit the information updates to the brain. In case of any medical damage in the cerebral peduncle, there is a loss in proprioception and acceptance of commands by the body. Similarly, if there is an injury to the body, it transmits the information to the brain and limits the movement of that specific part.
Posts You May Like to Read:




