Topics Covered
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation and swelling of the bronchial ducts (tubes), the air sections between the mouth and nose and the lungs. Specifically, Bronchitis applies to an ailment where the lining of the bronchial tubes becomes inflamed. People who have Bronchitis possess a reduced ability to inhale air and oxygen into their lungs; also, they cannot clear heavy mucus or phlegm from their breathing passages.
Undoubtedly you had your own discuss of colds. Maybe you even know somebody who had pneumonia. In between of these two situations is a sickness called Bronchitis, that could be more serious as compared to the common cold but not as threatening as pneumonia.
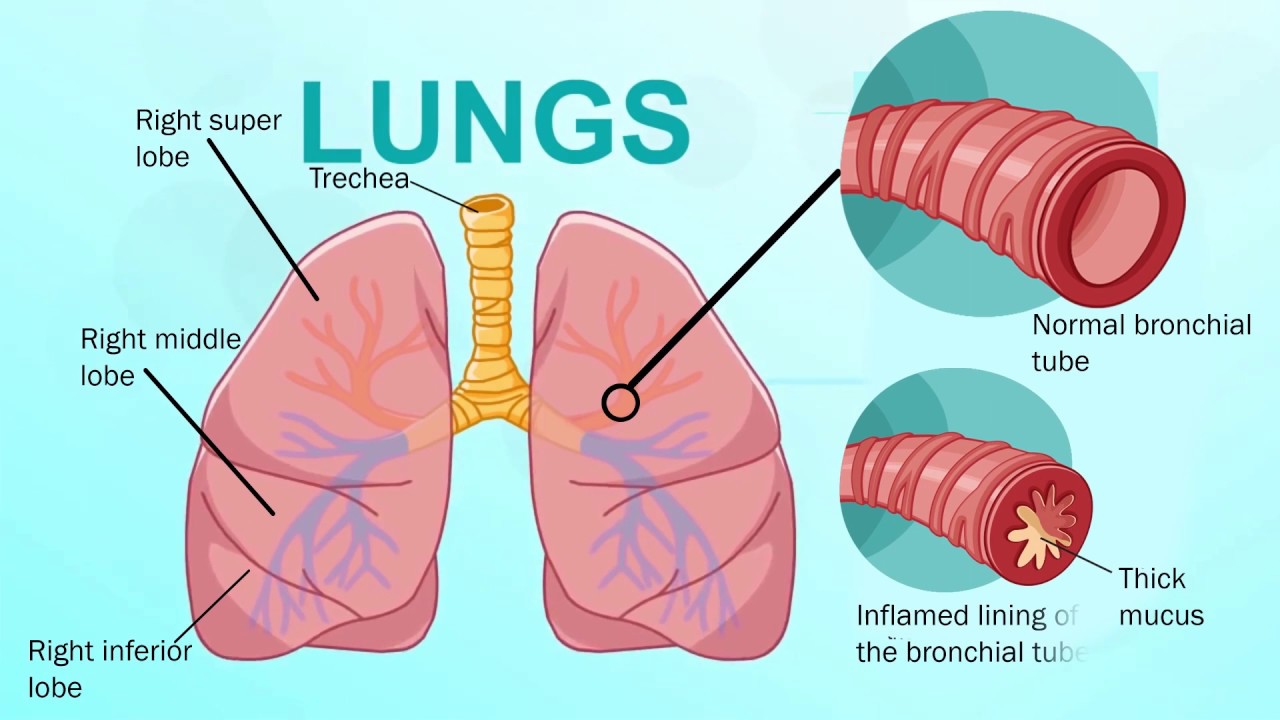
A cold or the influenza runs its course in a couple weeks, if you’re lucky. Thereafter, you’re back to normal. But at times you can get Bronchitis, too. That’s when your bronchial tubes, which carry air to your lungs, get infected and bulged up. You may end up getting an irritating cough and a much more mucus. You may get Bronchitis in other ways too.
There are Two Types of Bronchitis
Acute Bronchitis: This is the more common one. Signs and symptoms persist for a couple weeks, but it doesn’t generally cause any problems past that. Acute Bronchitis normally has a cough that can last around 3 weeks. In more than 90% of circumstances the cause is a viral infection. These types of viruses may be spread through the air when people cough or by direct contact. Threat factors include exposure to cigarettes smoke, dirt and dust, and other air pollution. A small number of cases are due to increased levels of air pollution or harmful bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae or Bordetella pertussis. Treatments for acute Bronchitis typically requires rest, paracetamol(acetaminophen), and NSAIDs to help with the fever.
Chronic Bronchitis: This one is more serious, in that it will keep coming back or doesn’t vanish at all. Chronic Bronchitis is referred to as a productive cough that can last for three months or more per year for at least two years. Most of the people with chronic Bronchitis have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD). Nicotine and tars smoking is the most common cause, with many other factors for example air pollution and genetics and heredity playing a smaller role. Treatments can include quitting smoking, vaccinations, rehabilitation, and often inhaled bronchodilators and steroids. Some individuals may benefit from long-term oxygen therapies or even lung transplantation.
Signs and Symptoms of Bronchitis
You’ll have a cough, and you may suffer from various problems with breathing. Signs and symptoms of both acute and chronic Bronchitis are as follows:
- Constant Coughing: A cough that may bring up a lot of mucus that’s clear, white, yellow, or green.
- Sneezing: You may sneeze often than earlier.
- Wheezing: A wheezing sound when breathing (may or may not be present).
- Fever: A low fever may or may not be present.
- Difficulty in Breathing: You may feel shortness of breath or uneven breathing.
- Chills: You May feel chilling with fever.
- Tightening of Chest: You can also suffer from tightening of chest.
- Pain in Body: Your body will start paining starting from chest to head.
- Sore Throat: Due to persistent coughing, you will have sore throat.
- Stuffy Nose: You may go through stuffy or runny nose.
- Symptoms of Sinus: There a slight chances of sinus symptoms also.
- Severe Headaches: Due to constant coughs, your head will suffer from pains.
- Nausea: You may feel tired or weakness.
While most of the signs and symptoms of Bronchitis normally get better within 2 weeks, coughing can be sometimes persistent for up to 8 weeks.
Causes of Bronchitis
Normally, the same viruses that make you suffer from cold or the flu can also cause you Bronchitis. Sometimes, though, bacteria are at the blame. In both the cases, as your body’s immune system fights with the germs, your bronchial tubes get swollen and make more mucus. That means you may have smaller openings of bronchial tubes for the air to flow, which can make it harder to breathe.
Bronchitis could be caused by either a virus or else bacterias, however viral Bronchitis is more common. Generally, Bronchitis is caused by the very same viruses that initiate the common cold or the flu. The virus is found in the millions of tiny droplets which come out of the nostril and mouth whenever someone coughs or sneezes.
All these droplets typically spread about 1m(3ft). They hang floating in the air for some time, after that land on surfaces where the virus can stay alive for up to 24 hrs. Anyone who touches these surface areas can spread the virus farther by touching other things.
If any of these things is experienced by you then, you have a bigger chance of getting Bronchitis:
- Weaker Immune System: This happens with grownups and people who have ongoing diseases, as well as toddlers and small children. Even a usual cold or cough makes it much more likely as your body’s by now busy fighting with those germs.
- Smoking: If you smoke cigarettes or live with a smoker.
- Place of Work: Your work surround things that bother lungs, such as chemical fumes or chemical dust (Examples: coal mining, animal husbandry).
- Pollution: You live in or travel at such a place with poor air quality or lots of pollution.
How Bronchitis can be Diagnosed?
Your medical professional is going to question you about your signs or symptoms of Bronchitis and he will probably carry out a physical examination. As many people that have acute Bronchitis will get much better within a shorter period, your doctor could possibly recommend the following lab tests when your signs and symptoms continue for a long time or become worse.
X-ray: X-ray of a chest area to make sure you haven’t developed pneumonia that is an extremely dangerous complication of acute Bronchitis.
Mucus (Sputum) Sample: Your physician can suggest testing a small sample of the mucus (sputum) that you are coughing up for some bacterial infections.
Spirometry (Lung Function Tests): Your doctor would recommend you check the state of the air passages of your lungs as well as exactly how well your lungs are working.
Throat Swab: This examination is performed to check out the probable factors that cause acute Bronchitis, such as influenza.
It is best to consult your doctor when you face the following circumstances:
• You seriously feel shortness in breathing
• You get pain while you breathe
• You have high fevers
• You are coughing up plenty of mucus or the mucus is blood-stained
• Your signs and symptoms are not improving
• You possess pre-existing heart or even lung disease (for example heart failure or asthma disease).
Treatment of Bronchitis
Treatment for Acute Bronchitis: Many people heal from acute Bronchitis with self-help strategies within few weeks. For those who have acute Bronchitis, your doctor may advise you to:
• Rest
• Drink Lots of Liquids
• Take pills such as Paracetamol to Lessen Pain and Fever
In many of the instances of acute Bronchitis you might not need antibiotics. Even so, if you are coughing up plenty of yellow or green sputum, you possess a high fever, you are particularly unwell, your Bronchitis might have a bacterial cause. In such cases, your doctor can prescribe you anti-biotics.
Treatment for Chronic Bronchitis: There are several options your doctor will recommend if you have chronic Bronchitis or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
- Treatment for Chronic Bronchitis: There are several options your doctor will recommend if you have chronic Bronchitis or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
- Giving up on smoking cigarettes can slower the rate that the disease gets progressively worse as well as should get better your signs and symptoms. It is probably the most important things that you can do to help in case you are a smoker.
- Medicines are useful to relieve signs and symptoms, avoids flare-ups, and strengthen lung functionality and quality of life. They are usually consumed in the form of an inhaler.
- Antibiotics are usually recommended to tackle flare-ups in people who have chronic Bronchitis.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programmes are intended to help improve signs and symptoms and level of quality of life for those who have COPD.
- A yearly influenza vaccination can easily protect against you from catching influenza in the winter season, it is advisable for people that have COPD. Vaccination against pneumococcal disease can be prescribed.
How to Prevent Bronchitis?
Among the most common factors that causes acute Bronchitis is influenza (the flu), therefore it’s a smart concept to possess a yearly flu vaccination. Immunization is generally advisable in autumn, so you are safeguarded over the wintertime flu season. Pneumococcal vaccination is likewise advised for many people. Being immunized can help protection against many strains of pneumococcal bacteria that usually cause pneumonia.
Consult your doctor regarding which vaccines are suitable for you. It’s also necessary to cut down on exposure to smoking. Quit smoking cigarettes if you are a smoker, and take measures to stay away from reflexive smoking.
See More Other Posts: